
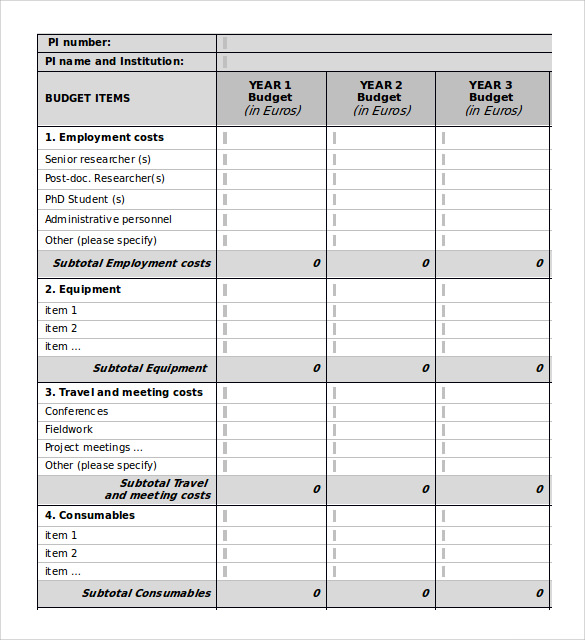
Yet, while the two go hand-in-hand, they are not the same. You can adjust your budget again during more profitable months.Financial plans and budgets can help you be financially successful now and in the future. During months when your business is slow, you’ll need to lower your flexible expenses. If you find it’s challenging to stick to the budget you created, remember that it will take time and ongoing adjustments to find the right balance. It’s important to continue tracking your revenue and expenses to make sure you’re sticking to your goals. Creating a budget is just the first step. You will need to lower your expenses or increase revenue (or, even better, do both) to make a profit. If the result is a negative number, your expenses are greater than your revenue. If the result is a positive number, congratulations - you should be on track to make a profit. It’s a simple step that can reveal how much profit you could be making. Once you’ve totaled up your revenue and estimated expenses, subtract the expense total from the revenue total to get the difference. It’s important to be as precise as possible, as expenses can vary greatly from month to month. Divide your expenses into fixed costs (those that don’t change from month to month, such as rent, salaries and insurance payments) and flexible expenses (costs that change, such as raw materials and commissions). The best way to do this is to track how much you spend in a month. To create a monthly budget, you should first determine how much money you make by listing sales, investments and any other revenue sources. The key to creating a successful budget is to add up all of your revenue sources over a 12-month period, forecast your expenses to estimate your profit (the difference between your revenue and costs), and frequently review your budget through monitoring monthly. Profit or Income – The amount remaining after you subtract revenue from expenses. Flexible expenses, which change from month to month, such as product or service costs and transportation.Fixed expenses, which stay the same from month to month, such as rent, salaries, insurance and accounting services.Expenses can be categorized in two groups: Revenue – The actual amount of money received through business activities, including selling products, investments, interest on savings, dividends and other sources.Įxpenses – All costs associated with running a business, including direct costs (materials or supplies), recurring expenses (rent or electricity), long-term assets that will help your business for years, but are harder to sell (buildings or equipment), and financial expenses, such as loan or interest payments. Understanding these key components will help as you begin to build a budget: Set short- and long-term goals for business growth.This will help you stay on track to achieve your goals. Revisit and rework your budget monthly, quarterly or after changes to your business, such as big expenses, occur. Using a budget can help you make more informed financial decisions.įor example, if you know how much money you earned and spent every week for the last several months, you’ll know how much you can afford to spend if you want to hire a new employee.īudgeting is an ongoing process rather than a one-time exercise because your business revenue and expenses could change at any time. It allows you to oversee and better understand whether your business has enough revenue (incoming money) to pay its expenses. Creating a budget is an important pillar of your overall success and security.
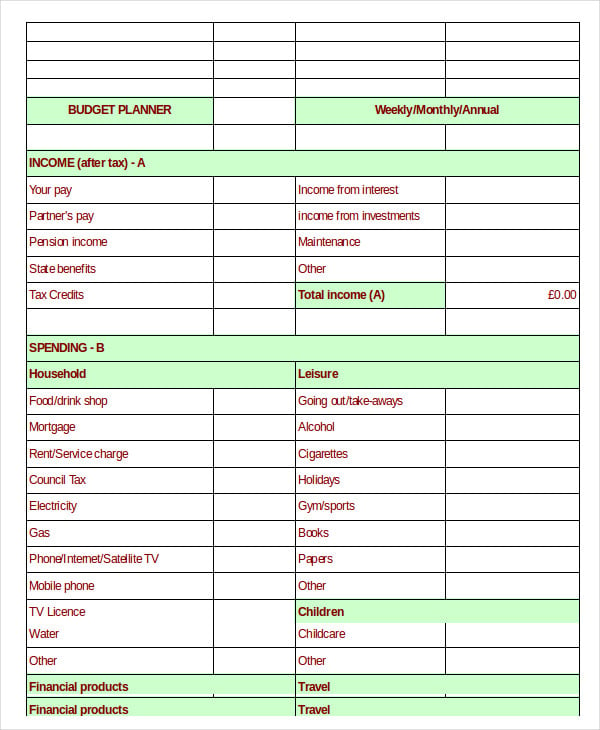
What is a budget and why is it important?Ī budget is a tool to track when and how you earn or spend money.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
